Penetrant Lines for Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection (FPI)
Test stands and plant construction for the dye penetration process (NDT)
Systems for penetrant testing (also known as PT penetrant testing) are most frequently used in the field of non-destructive material testing to carry out the crack detection process. The penetrant test or penetration test is a highly sensitive, non-destructive test method to determine surface defects that are open to the outside (such as cracks, pores, voids or binding defects). It is a quality assurance instrument, especially for components and workpieces for safety-relevant areas, which otherwise can cause high follow-up costs in the event of errors. The plant construction for the dye penetration process includes individual components such as pre-cleaning, drying ovens, etc. When designing and planning individual modules, the Ril-Chemie team always has the overall system in mind in order to enable the best possible processes for you as the user.
With regard to costs and overall budget planning, not only the size of the system but also the consumption of chemicals and operating costs generally play an important role. We take these factors into account right from the start over the entire course of the project in order to be able to implement the goal of a cost-effective and at the same time user-optimized system for you.
Regardless of whether you are planning a completely new penetration testing system or want to expand or convert an existing one – we are there for you.
Maximum process reliability with user-centered functionality
Economically efficient systems for dye penetrant testing with innovative features
Trouble-free continuous operation, guaranteed by years of practical experience
Penetrant Lines for FPI
-
manual
-
semi-automatic
-
full-automatic
-
components

Highlights of the SECU-CHEK systems for optimized dye penetrant testing (NDT)
- Safe, quick and easy testing of the wetting and the test agent application
- Constantly excellent intermediate cleaning at the washing area
- No risk of overwashing
- Minimized background fluorescence in the evaluation booth
- Fatigue-free, high-contrast evaluation up to 10 times faster
Many practical advantages with the "state-of-the-art" SECU-CHEK systems for dye penetrant testing
- Seamless Industry 4.0 – integration / PLC control / robot programming and much more.
- Electronic display and monitoring of all relevant process parameters (e.g. Nadcap CAP checklist AC7114 / 1 point 4.2.3.1 temperature monitoring of the furnace, etc.)
- Emulsifier concentration with electronic display and monitoring
- Integrated adaptation time signaling for compliance with the relevant test standards
- Different types of water treatment / direct discharge
The planning, conception and installation of a system for PT penetrant testing requires a lot of expertise and practical know-how so that you as the user can work optimally with it. Choose our offer for a SECU-CHEK PT system that is precisely tailored to your NDT requirements and trust our experience.
The requirements for component testing and thus for dye penetrant testing systems are increasing from year to year, especially in view of the increasing networking and digitalization with Industry 4.0. With our customers from the high-tech sectors, including the aerospace and automotive industries, we, as a full-range supplier with the appropriate advice and expertise, implement these requirements precisely, including the development of individual customized system solutions for dye penetrant testing.



In addition to manual, semi or fully automatic penetration systems, we also supply dryers, activated carbon filter systems for water supply and disposal, as well as all other upstream and downstream systems, modules and logistics components: pre-treatment systems, metal baskets and goods containers and much more.
Our crack detection systems contain innovative automation technology and are individually tailored to your requirements – safe, well thought-out and future-proof.

What types of systems are there for penetrant testing?
Degree of automation / economic efficiency
- Manual penetration systems: for individual parts and small series (e.g. classic test bench / test stand for penetrant testing)
- Semi-automatic penetration testing systems: usually with different components in use / changing component portfolio (semi-automatic systems e.g. with manual input / output and automatic penetrant application)
- fully automated penetration line with transport baskets etc .: designed for bulk parts
Regardless of the degree of automation of the Fluorescent penetrant system, there are many ways to achieve high efficiency, process reliability and user-friendliness.
We would be happy to advise you to ensure that the individual components work together optimally.
Many options: Starting with the integration of an E-Static developer station to the selection of the right UV-LED modules to control, monitoring and much more. There are many design options to achieve a high ROI (Return On Investment).

Frequently asked questions when planning and designing an system for dye penetrant testing
- How do I determine the correct size of the FPI system?
- How flexibly adaptable and expandable will the penetration testing system be in the future?
- What are the key functions that are needed in practice? Am I really up to date with what I know about the optimal design of the system?
- Which modules do I need for the system for dye penetrant testing? What is required for our special test situation?
- Are the individual components compatible with each other if I assemble the dye penetrant testing system myself?
- Who will take care of setting up the dye penetrant testing system including instruction?
- What UV illumination and intensity do I need in the evaluation cabin for reliable test results?
- Where / how are the UV-LED lamps and controls integrated to enable efficient work processes?
- What mounting options and free spaces are there in the evaluation cabin for the UV-LED modules?
- Do the processes and security mechanisms of the individual components correspond to the requirements that we have to meet?
- Does my budget plan fit for the overall project?
- What happens to unexpected additional costs if, contrary to expectations, individual components are not compliant?
- Can I keep to the schedule until the system for the dye penetration process is put into operation?
- Who guarantees the functionality and practicality of the entire penetrant testing system?

Conception, construction and commissioning of your dye penetrant testing system from one single source. Planning security and guaranteed practical suitability with SECU-CHEK.
"The SECU-CHEK technology enables you to have a system perfectly adapted to your test situation for liquid penetrant testing as a complete system - and that with personal project support from A to Z by our NDT experts"
Crack detection systems based on the penetrant method - possibilities and examples

fully automatic system for the dye penetration process

Test table for the FPI penetrant test

Activated carbon filter system Penetration method / crack test

Standards and norms for the PT penetrant test (penetrant - developer - cleaner): ASTM E1417, DIN EN 571, DIN EN ISO 3452
The penetration test (PT crack test) must conform to the ASTM E1417 standard and is standardized in accordance with DIN EN 571 and DIN EN ISO 3452. The parameters and settings are determined for the application, with regard to the sprays, brushes, fill levels and also for the times of the individual process steps, including the temperatures to be maintained.
These specifications may vary depending on the application areas, the industry and the clients. SECU-CHEK ensures that you comply with all relevant requirements and that you can successfully complete upcoming audits etc.
With SECU-CHEK systems for fluorescent penetrant testing you are always up to date, also for future norms and standards in addition to ASTM E1417, DIN EN 571 and DIN EN ISO 3452. Other important standards are, for example, MIL-I 25135E, MIL STD 6866 , AMS 2644, DIN EN 571-1. Compliance with all European regulations for the penetrant testing systems from SECU-CHECK with regard to occupational safety, operational safety and ergonomics are a matter of course.
Further advantages of the SECU-CHEK penetrant testing systems
- Penetration testing systems with intelligent, innovative automation (e.g. connection of PLC control and much more) to reduce personnel costs
- FPI penetrant testing systems with optimal, user-friendly working convenience
- Reliable traceability and reporting when using the SECU-CHEK penetrant testing system
- Low consumption of chemicals in the penetrant testing system thanks to the use of E-Static developers and much more.
- low operating costs compared to conventional penetrant testing systems
- good durability and a high level of safety with the SECU-CHEK penetrant testing system for your entire process
SECU-CHEK offers high quality test equipment systems for penetrant testing (PT). We cover all types, levels and processes of penetration testing systems, of course also requirements with aviation approval. The crack indicators can be implemented in all variants of the penetrant test: electrostatic with dry developer, wet developer based on solvents or with water based developers.
The modular structure of our penetrant testing systems is the basis for problem-free expansion at a later date. Short walking distances and optimal use of the possible floor space are a matter of course.

Industry 4.0 in plant construction for dye penetrant testing
Systems for dye penetrant testing are increasingly networked and automated in the course of digitalization. Industry 4.0 means that relevant parameters and values are transferred from time to time to the corresponding interfaces to the crack detection system, so that you benefit from an overall system in which the different processes are more closely interlinked. This increases the transparency, i.e. the catchphrase “Industry 4.0” for fluorescent penetrant inspection conceals great potential and a lot of relief for you and your employees and colleagues.
Measured values are transferred automatically, for example, certain processes such as the evaluation in the penetration test system can only be started when certain parameters are correct (e.g. the adaptation time signaling has enabled this).
With Industry 4.0, the penetration line supports process security and makes work easier overall. Higher productivity while reducing user stress at the same time are important aspects that SECU-CHEK would be happy to tackle with you on your next crack detection system project.
Industry 4.0 penetrant testing systems from SECU-CHECK increase productivity and process reliability and reduce your material- and energy-consumption
More overview & Control
- Electronic display and monitoring of the relevant process parameters: e.g. temperature monitoring, among other things, of the furnace in the penetrant testing system (Nadcap CAP checklist AC7114 / 1 point 4.2.3.1)
- PLC control
- digital display
- Calibratable crack detection system
Higher transparency / measured values
- high quality PT100 and PT1000 sensors for precise and reliable measurement
- electronic display and monitoring of the emulsifier concentration:
- Digital refractometer: correct display of the emulsifier concentration without conversion and without using a table
- Inline refractometer: fully electronic monitoring by the central system control (SPS / PLC)
- automated reporting
- direct process insight and extensive figures “on the fly” in the dye penetration test system
Process security for high-security applications
- Integrated adaptation time signaling integrated into the luminaires (optionally adjustable by the user to 1, 3 or 5 minutes with the UVE UV-LED luminaire series. Further adaptation times can be set ex works)
- Adaptation time signaling integrated into the system control and monitoring by the central PLC control with presence monitoring and release of the system only after the adaptation time according to NADCAP AC 7114/1 (4.2.8) and 7114/2.
- Prevent NCR audit finding (NCR = non-conformance reports). Compliant calibration etc.
PLC control of testing systems for dye penetration methods
Shorten walking distances and process steps with a central PLC control
- Monitoring of all parameters
- Control monitors with the most important test parameters can be viewed from anywhere
- Operation and setting via the central operating unit as well as optionally further remote controls for optimal processes
- Documentation of all parameters and values such as temperature monitoring, emulsifier concentration, etc.
Many variants of penetrant testing systems - individually tailored to your requirements
Examples of penetrant testing systems
- Penetration test station for the use of the fluorescent penetration method or the red and white crack test, optionally with E-Static developer module, designed for components up to 1000kg
- Test table / penetration table (red / white penetration method or fluorescent test system) with electro-mechanical height adjustment (stainless steel construction with grids that can be positioned on different levels, suction with filter, etc.)
- Manual penetrant testing system for the fluorescent test procedure with electrostatic spray system for the developer (E-Static developer station)
- Semi / semi-automatic systems for dye penetrant testing for the application of fluorescent penetrant testing including E-Static developer system The test system can optionally be equipped with different test equipment (one E-Static gun for each test equipment)
- PT penetration station with special trolleys and transport baskets that are used for loading the system, for further transport after the testing process and also within the system during the penetration testing process
Module overview for crack detection systems based on the penetrant method
The crack testing components listed below are individually combined and tailored to your process.
charging station / pre-cleaning (especially for automatic penetration lines)
- pre-cleaning areas / Pre-cleaning place
- pre-cleaning systems
- various design variations can be implemented for any requirements
washing station intermediate cleaning
- split into two or more modules / cleaning stations for automatic penetration stations:
- Pre-wash station / washing up
- Rinse station / rewash / afterwashing
Resource-saving: The rinsing is carried out by a pressure-controlled spray head with a sophisticated pump control. In automatic lines, the flush water supply uses recycled water for the initial partial flush, followed by a fresh water flush.
Penetration station / developer spray station
- Penetrating: spraying or immersing the components
- with draining area
- incl. suction device
- with splash guard
- for penetration (red or fluorescent)
- also possible as a variant for penetration using the immersion process
dry developer station
- for evaluation / inspection
- check the parts for complete coverage
- with electrostatic spray gun to mend
- optionally including suction device, e.g. PLC-controlled HEPA filter system
- optional 360 ° rotating plate for unrestricted testing
- optional foldable splash guard
- optionally incl. dust collector with HEPA filter
- dry development white
Emulsifier station / emulsifier basin
- apply the immersion basin to the emulsifier
- optional pneumatically or electrically powered immersion system for raising and lowering the baskets
- optionally PLC-controlled to enable uniform acceleration and processing time during transport and to ensure that the process specifications specified in ASTM 1417 are adhered to
- optional PLC control and control that the parts are rinsed within the specified 2-minute window after emulsification
- after the emulsifier comes the stop bath
Emulsifiers are auxiliary chemicals that are required in non-destructive testing (NDT) in order to be able to wash off the excess of the non-water-washable, post-emulsifiable penetrant from the test surface.
Drying station / drying oven for penetrant testing NADCAP compliant
- normally in the range of approx. 60-70 °C
- optionally temperature-controlled according to pre-settings at start (PLC control)
- the drying ovens of the crack detection systems can be operated with electricity, gas or steam
- optional PLC-controlled calibration connection for checking the oven temperature
- highlights of the SECU-CHEK drying ovens for penetrant testing:
- even heat distribution
- individual production
- NADCAP compliant
- central control, optionally with intelligent PLC control
- adhesive water dryer
- trough dryer, cabinet dryer
- continuous oven and continuous dryer as circulating air chamber dryer
- drying station for preparation before the actual penetration test line: Temperatures of 100 and more degrees for preparation / pre-cleaning, depending on what the parts have to be cleaned with.
Observation station / test bench for inspection
- test station for penetrant testing according to EN ISO 3452
- test table as mobile and stationary version possible
- incl. Exhaust air / suction (stationary or mobile, suitable for solvents with activated carbon filter for circulating air)
- in larger penetration testing systems, there are also several viewing areas in blackout cabins with UV lighting
Loading and unloading systems: goods racks / transport baskets / container construction
- Material: stainless steel or plastic
- open or closed
- round or rectangular
- optionally reinforced, with special surface coating, insulation and much more.
- different bottoms (flat, sloping, funnel-shaped, curved dished bottom according to DIN 28011, …)
Container construction for penetration testing systems – individually manufactured according to your requirements. We are happy to offer you all-round service with the technical design on site, including production and assembly, so that you can optimally charge your system for the penetrant test and integrate the most efficient test possible into your entire company process.
Evaluation booth: inspection & evaluation (+ discharge with fully automatic dye penetrant testing systems)

- the latest, reliable UV-A-LED high-performance technology
- LED-UV lamp modules with optimal illumination in the required intensity (strong, extremely even, low-shadow illumination with UV formity technology)
- Revolutionary, dimmable white light, steplessly switchable (optional)
- Inspection with black light, air conditioning on request
- Multi-dimensional, also angled alignment possible in the crack detection system
- Space-saving integration in the evaluation cabin for maximum user-friendliness
- optionally several test stands for different types of components
- Integration of process monitoring
- Splashproof (IP67) and test equipment resistant
- UV-LED lamps optionally active fan cooling for a particularly long service life
- All intensity requirements of the Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection (FPI) are met
- conforms to ASTM E3022 standard as well as Roll-Royce RRES90061
- optional system health monitoring
- Certification possible for all common standards, approved for all NDT applications
- Different UV intensity levels for testing the wetting and intermediate cleaning in one cabin
- PLC control (e.g. activation of washing water only after switching on the UV lighting to ensure process safety)
- and much more.

Activated carbon systems for water supply and -disposal in the dye penetration process - well thought-out water treatment concepts from SECU-CHEK
Water treatment / activated carbon systems
- Water treatment system with activated carbon cleaning (carbon filtration unit)
- Removal of water-washable and post-emulsifiable penetrants and excess rinse water.
- Dirty and service water separately in separate containers
- optionally with coalescence filter for optimized water supply and disposal
- powerful pump system in different versions (up to 100 liters per day, up to 500 liters per day, up to 1000 liters per day and more)
- containers and concentration monitoring for biodegradable test equipment
- indirect discharge into the sewerage station and sewage treatment plants
- conversion and expansion of existing activated carbon systems
SECU-CHEK offers the development of water treatment concepts including seamless integration into the overall system of the crack detection system as well as conversion and expansion of activated carbon systems.

Main areas of application of systems for dye penetrant testing FPI
Systems for dye penetrant testing FPI are used in a wide variety of areas. The inspection of components using fluorescent penetrants is used to avoid failures during operation:
- Penetrant testing systems for aviation and aircraft construction, helicopters, aircraft components
- Penetration systems for space travel, rocket construction
- Penetrant testing systems in the defense and military sector
- Dye penetrant testing for the automotive industry, including off-road vehicles, engine parts, wheel hubs, brake parts
- Test stations in mechanical engineering
- Crack detection systems in shipbuilding
- fluorescent penetrant testing in the energy sector and nuclear reactor construction
- simple penetration test stations or semi / semi-automatic penetration test systems in the field of metal processing, welding and much more.
- Systems for crack detection designed for the electrical engineering industry
- Medicine dye penetrant test (fluorescent penetrant test)
- System for dye penetrant testing FPI for container construction
- Testing systems with fluorescence penetrant testing for cast parts, turbines
- Test stands for steel, gray and malleable cast iron, overrolling and much more.
- Stationary penetration systems for landing gear parts in freight transport and rail operations, aircraft landing gear
- Dye penetrant test (fluorescent penetrant test) for brake parts
- Crack detection systems based on the penetrant method also for non-metallic materials such as plastic and ceramics

E-static spray systems from SECU-CHEK for the efficient and uniform application of dry developer (powder developer) and penetrant (penetrant) during dye penetrant testing
Optimized electrostatic spraying for FPI
Electrostatic spraying or electrostatic coating offers many advantages over other application methods. Particularly when it comes to penetrant testing, it is characterized by a particularly high level of economic efficiency, has an above-average application efficiency with a better spray pattern and an extremely homogeneous layer thickness. E-static systems from SECU-CHEK offer great time savings, lower material consumption and reduced disposal costs.
The principle of an E-Static spray system is that the negatively charged penetrant particles hit a grounded test piece. When they meet, a force field is created, which ensures the so-called wrap-around effect and, with minimized droplet size, all sides of the workpiece can be coated very quickly at the same time with the lowest material costs.
- manual E-static spraying system for test equipment application
- manual electrical static for dry developers
- semi-automatic electrostatic spray systems for test equipment application
- semi-automatic electrostatic application systems for dry developers
- Electrostatic application systems specially developed for use with PT products (penetrant and developer)
- Components for electrical static systems (e-static systems) for application for expansion, modification, etc.
- tailored to your requirements for all types of penetrant testing: dye penetrant testing, fluorescent penetrant testing
As a system provider, SECU-CHEK advises you on your electrostatic spraying system and offers you a manual, semi-automatic or fully automatic system that exactly meets your requirements and effectively supports you in your work, and within your budget. Here you can find further details on electrostatic spray systems for industrial dye penetrant testing.

Modifications & adjustments / further services for penetration systems and crack detection (dye penetration method)
With SECU-CHEK as a partner, we get the best out of your machine park for dye penetrant testing. Regardless of whether you need higher capacities in the meantime or certain standards and process requirements have changed:
- Modernization and overhaul of your system for penetrant testing
- Expansion of penetration systems with components for more efficiency and higher capacity
- Relocation of systems for dye penetrant testing
- Certification / recertification reliably from a single source by SECU-CHEK, e.g. CE conformity and much more.
- incl. legal documentation from our experts
Further services in the field of dye penetrant testing and industrial penetrant testing:
- Analysis and monitoring of test equipment from all manufacturers
- Training and support in the selection of test equipment and change-over
If you are looking for industrial penetration systems and are active in the B2B-sector, you are welcome to contact us on business and receive an offer for penetration systems. The advantage of SECU-CHEK as a system provider is that we offer all components and modules for dye penetrant testing systems and penetration systems from a single source, including products and services in general from the area of dye penetrant testing and non-destructive testing (NDT). This gives you competent support and advice on the subject of penetration systems. We will be happy to help you even if your already installed penetrant testing system has not been delivered and installed by us.
Many visitors would like to find out more about the topic of penetration systems and the dye penetration process as well as test stands etc. and come to us using the following search terms:
- Systems for dye penetration testing and penetration testing
- Penetration systems and penetration lines
- Systems for penetration testing and penetration machines
- Penetration systems using the penetration method
- Penetration machines and systems for the fluorescent penetration process
- Systems for crack testing and system construction, penetration methods, crack testing machines
An essential point that many of our customers in the field of plant construction for dye penetrant testing point out is the desired durability and long-lastingness. The penetration systems should be robust and valuable, as they will be used in daily rough industrial use and such a system for crack detection is an investment over many years. You can’t afford to make any mistakes. It is precisely for this reason that we are pleased that we receive many recommendations and that we can be an equal partner for the penetration process with competent advice and long-term support in the field of penetrant testing plant construction.
Penetration method / crack detection - knowledge and detailed information
The procedure of liquid penetrant testing: Difference between dye penetrant testing and fluorescent penetrant testing
The non-destructive crack test according to the penetration method – explained in a simple and understandable way: The penetrate (liquid) is applied to the corresponding spot or the entire component to be tested after the test piece has been mechanically cleaned. This penetrate liquid penetrates into existing cracks after some time and remains in the cracks after the penetrant has been washed off the surface. A developer liquid causes the remaining penetrant to swell and thus makes even the smallest cracks, previously invisible, visible to the naked eye.
Depending on the method used, the cracks are reddish in color ( Red-White Penetration Test ) or with the aid of UV lamps, the cracks are highlighted again by fluorescence (Fluorescent penetrant test). The procedures and methods are all based on the same principle, regardless of whether you are working with a manual penetration system, a semi-automatic penetration testing system or a fully automated system for penetration testing (penetration line).
The crack detection agent usually consists of three components, and no more complicated equipment or similar is necessary:
- Penetrant
- Cleaner
- Developer
In order to meet certain norms and standards, however, test bodies and control bodies are also used for the penetrant test.
The penetration or penetration process PT is based on the physical law of capillary action, can be used universally and has no limits on the materials to be tested.
Color penetration process (red-white)
- in daylight > 500 lux
- red penetrant
- white Developer (fine-grain powder, often based on lime, different types depending on the method)
- application in the penetrant testing system with a brush, dipping or spraying
- high color contrast red-white
Fluorescent penetrant process
- in the dark / darkened evaluation booth < 20 lux
- penetrant fluorescent under UV radiation
- much more sensitive than the red-white dye penetrant test
- application in the penetrant testing system with a brush, dipping or spraying
- very high contrast due to the darkness and the color fluorescence
- the human eye reacts much more sensitively to this luminance contrast than to color contrast
- is used especially in high-security areas such as the aerospace industry, but also the automotive industry and the energy sector

General classification of the penetrant method in the non-destructive testing method (NDT testing methods)
NDT (non-destructive material testing) is a solid basis for success in all industries, as it increases operational reliability, quality assurance can be implemented in a practical manner and high costs can be reduced through preventive measures. The following summary of the non-destructive test methods and the classification of the penetrant test in this context gives you an overview:
Penetration testing
- With the dye penetrant test, cracks or pores in the material surface are made visible
- Ideal for examining welded joints, castings and mass production, turbines and non-metallic materials (plastics, ceramics)
- After using penetrant, developer, cleaner, a visual inspection is carried out
- Variant: fluorescent penetration test under UV light with fluorescent penetrant
Eddy current testing
- Impurities and damage to an electrically conductive test piece have a different conductivity than the base material itself
- When an alternating voltage coil is applied, so-called eddy currents and an additional magnetic field occur
- Changes in the second magnetic field thus indicate soiling etc.
- Eddy current testing is also used to determine material properties and to check for mix-ups
Magnetic particle testing
- Finding surface cracks in ferromagnetic materials (steel)
- Application of magnetizable particles to the test surface
- Introducing a magnetic field into the test piece
- Cracks occur as a magnetic leakage flux and thus become visible
- can be used for more complex materials and unprocessed surfaces
Radiographic testing
- Error checking regarding the strength of materials
- Radiographic testing is a volumetric method for detecting voluminous defects
- X-rays are used to discover hidden inhomogeneities in the material
- various exposure methods (real-time, gamma or x-ray tubes, etc.)
- the data is saved on film or digitally and evaluated using norms and standards
Ultrasonic testing
- for the detection of inhomogeneities on the surface and the cross-section of the test material
- Measurement takes place with an ultrasonic pulse of the pulse-echo technique or the transmission technique
- Position, shape and size of the defect can be analyzed with the ultrasonic test
- Further ultrasound techniques: Phased Array and Time-of-Flight Diffraction Ultrasound (ToFD)
Visual inspection
- Evaluation of quality features of the surface of the component to be tested
- Visual NDT inspection with the human eye or magnifying glass / microscope etc.
- The visual NDT inspection comes before all other procedures
- Results of the visual NDT test as an important basis for further test methods
Advantages of the penetrant test (PT) in practice
The dye penetrant test (and also the fluorescent penetrant test) offers many advantages. For example, any material can be examined, including materials without ferromagnetic properties, such as the magnetic powder MT test, such as aluminum, copper, non-magnetic austenitic steel, plastics, glass and ceramic test pieces. It is also a cost-effective test method because relatively few devices are required for testing. So also ideal for mobile use in practice, e.g. on a construction site or in difficult-to-access areas of a nuclear power plant or other more complex units.
Here is a brief overview of other advantages of the penetrant test:
- any material can be reliably examined
- Mobile and flexible testing method
- There are no radiation protection regulations to be complied with
- Only one work process necessary to visualize all errors on the surface
- simple, inexpensive test method with little effort
Use of the penetrant method for the following materials
- Steel (alloyed, unalloyed)
- ferromagnetic materials
- Non-ferrous metals (aluminum, copper, …)
- Plating
- Steel, gray and malleable cast iron
- Welds
- Steatite
- Plastics
- Ceramic
- a variety of other solids and materials
Attention: with the penetrant test and therefore also in general with all crack detection systems, no porous materials can be tested and, for example, also no Teflon.
Possible error messages during the penetrant test
- Cracks (cold cracks, hot cracks, grinding cracks)
- Bowls
- Overrolls
- Pores (of various sizes) and pore nests
- spongy structure
- Stress corrosion cracking
Norms and standards for crack testing (Annexes PT dye penetrant testing and crack detection agent)
The crack detection agents, consumables and the systems from SECU-CHEK for the PT dye penetrant testing are recognized test agents in non-destructive material testing with all required approvals for the penetrant test:
- Penetration method according to DIN EN ISO 3452-1: 2013 (replacement for DIN EN 571-1: 1997 – 03)
- SAE AMS 2644
- MIL-STD-6866
- MIL-I-25135E (replaced by SAE AMS 2644)
- DIN EN 571-1
- Compliance with all European regulations (occupational safety, operational safety, ergonomics, …)
Here all standards for penetration testing are listed again:
- German Institute for Standardization (DIN)
- DIN 25435-2, Recurring tests of the components of the primary circuit of light water reactors – Part 2: Magnetic particle and penetrant testing
- DIN EN 1371-1, Foundry – Penetrant testing – Part 1: Sand, gravity mold and low-pressure mold castings
- DIN EN 1371-2, Foundry – Penetrant testing – Part 2: Investment castings
- DIN EN 2002-16, Aerospace – Metallic materials; Test methods – Part 16: Non-destructive testing, liquid penetrant testing
- DIN EN 10228-2, Non-destructive testing of steel forgings – Part 2: Penetrant testing
- DIN EN ISO 10893-4 Non-destructive testing of steel pipes – Part 4: Penetration testing of seamless and welded steel pipes for the detection of surface imperfections
- DIN EN ISO 3059, Non-destructive testing – penetrant testing and magnetic particle testing – viewing conditions
- DIN EN ISO 3452-1, Non-destructive testing – Liquid penetrant testing – Part 1: General principles
- DIN EN ISO 3452-2, Non-destructive testing – Penetrant testing – Part 2: Testing of penetrant testing media
- DIN EN ISO 3452-3, Non-destructive testing – Penetrant testing – Part 3: Control bodies
- DIN EN ISO 3452-4, Non-destructive testing – Liquid penetrant testing – Part 4: Devices
- DIN EN ISO 3452-5, Non-destructive testing – Liquid penetrant testing – Part 5: Liquid penetrant testing at temperatures above 50 ° C
- DIN EN ISO 3452-6, Non-destructive testing – Liquid penetrant testing – Part 6: Liquid penetrant testing at temperatures below 10 ° C
- DIN EN ISO 12706, Non-destructive testing – liquid penetrant testing – terms
- DIN EN ISO 23277, Non-destructive testing of welded joints – Penetrant testing of welded joints – Permissible limits
- DIN CEN / TR 16638, Non-destructive testing – penetrant testing and magnetic particle testing using blue light
- ASTM International (ASTM)
- ASTM E 165, Standard Practice for Liquid Penetrant Examination for General Industry
- ASTM E 1417, Standard Practice for Liquid Penetrant Testing
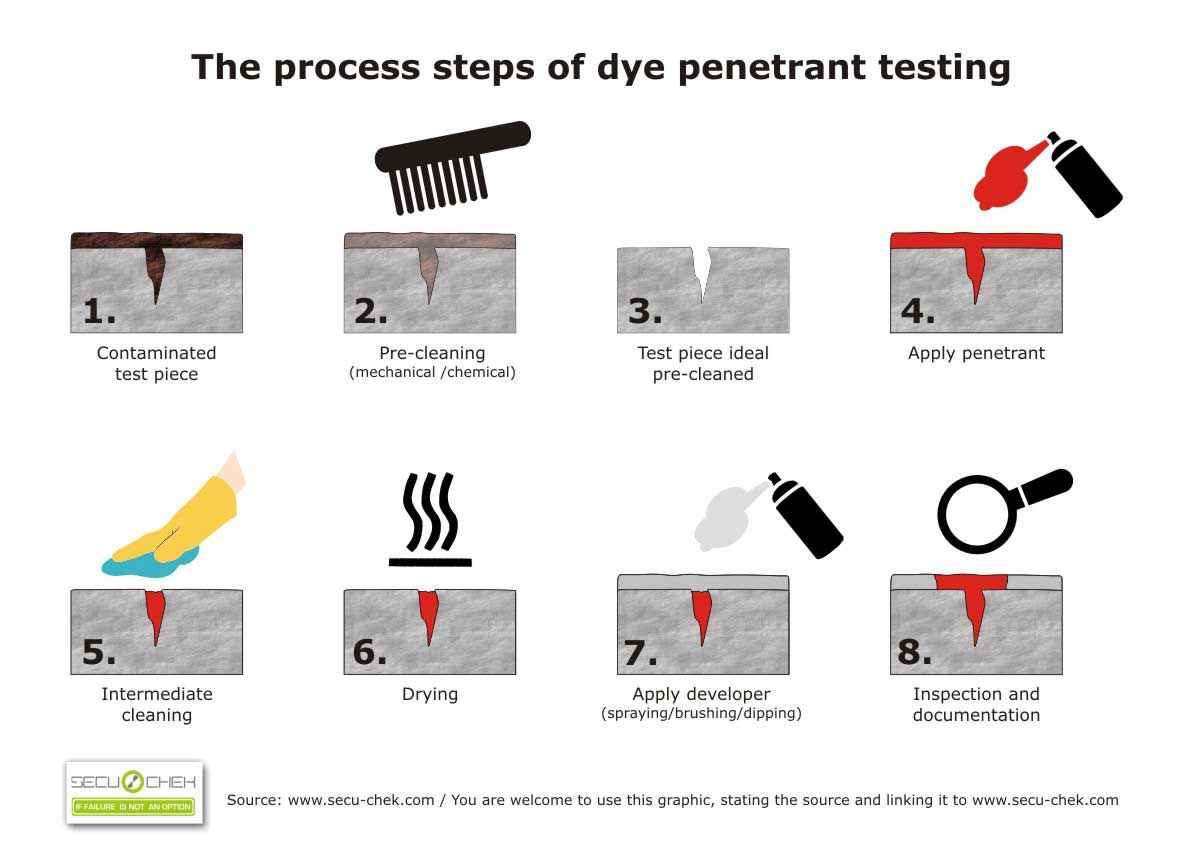
The process steps of dye penetrant testing / crack test procedure
Procedure for crack testing in detail:
- Contaminated test piece: the material can be contaminated by a pre-treatment, so that there is dirt in the cracks.
- Pre-cleaning (mechanical / chemical): Preparation and cleaning of the surface to be tested, e.g. B. by brushing, grinding, blasting or a chemical cleaning agent. Sometimes also drying at up to 100 ° C in the oven and cooling to 40 ° C.
- Test piece ideally pre-cleaned: the material to be tested was returned to its original state after the pre-cleaning and can now be fed to the test, i.e. it is delivered to the crack detection system.
- Apply penetrant: this is the so-called penetration phase, in which the penetrant is applied to the entire surface of the material by dipping, pouring or spraying and can penetrate into the cracks, etc. (“penetrate”). This is followed by a sufficiently long exposure time, which varies depending on the material and requirements / standards (usually in the range of 5-60 minutes).
- Intermediate cleaning: cleaning of the surface, excess penetrant is removed (e.g. with a lint-free cloth or sponge or washed off with water). Depending on the process sequence, an intermediate step “emulsifying” including post-washing takes place when the emulsifying process is used. Important: The penetrant remains in the cracks regardless of which process is used.
- Drying: The drying in this process step of the penetrant test usually takes place at 60 ° C in the oven or by evaporation or compressed air etc.
- Apply developer (spraying / brushing / dipping): The developer is applied and allows the penetrant to swell. The penetrant pulls the developer out of the cracks like blotting paper and thus enlarges even the smallest cracks as visible lines.
- Inspection and documentation: Crack indication with the developer (wet developer / dry developer). The test piece is examined for signs of cracks and breaks in the observation station, including the corresponding documentation such as photos or videos. With the fluorescent penetrant test, the inspection is carried out with a UV lamp, otherwise with the red-white method simply with the naked eye.
Classification of the test equipment in the penetrant test procedure / classification of the penetrant systems according to DIN EN ISO 3452-2
Which variants or product families are used for the penetrant method depends on the individual requirements for the sensitivity of the method, environmental protection, work safety and the quality of the materials to be tested.
- Penetrant (I, II, III)
- I: Fluorescent penetrant test equipment
- Sensitivity class ½: insensitive
- Sensitivity class 1: slightly sensitive
- Sensitivity class 2: moderately sensitive
- Sensitivity class 3: highly sensitive
- Sensitivity class 4: extremely highly sensitive
- II: Dye penetrant testing agent
- Sensitivity class 1: normal
- Sensitivity class 2: highly sensitive
- III: Penetrant for two possible uses (fluorescent dye penetrant test)
- Sensitivity class 1: normal
- Sensitivity class 2: highly sensitive
- I: Fluorescent penetrant test equipment
- Intermediate cleaner (A, B, C, D, E)
- A: water
- B: lipophilic emulsifier
- C: solvent (liquid)
- Class 1: containing halogens
- Class 2: not containing halogens
- Class 3: for special purposes
- D: hydrophilic emulsifier
- E: Removable with water and solvents
- Developer (a, b, c, d, e, f)
- a: dry developer
- b: water-based wet developer, water-soluble
- c: water-based wet developer, suspension
- d: solvent-based wet developer (non-aqueous for type I)
- e: Solvent-based wet developer (non-aqueous for type II and type III)
- f: for special purposes e.g. removable developer
The method with penetrant testing agent as well as water and solvent removable intermediate cleaner and solvent-based wet developer is used most frequently (i.e. (II) III E e; Source: Wikipedia )
An overview with the corresponding designations of the AMS 2644 E can be found here: Classification of penetrant testing systems according to DIN / EN / ISO 3452-2 and AMS 2644-E (successor to the MIL-I-25135 standard)
Comparison of the test sensitivity of the different penetrant methods (color penetrant test vs. fluorescent penetrant test)
After we have presented the advantages and disadvantages of the various penetration methods, the aspect of test sensitivity is of course very interesting. How do the differences look in a specific example? In the following video, the color penetrant test (red-white method) and the fluorescent penetrant test are carried out on one and the same test piece, so that the visual difference emerges clearly:
The photo on the left shows the red-white penetrant test, in the middle the fluorescent color penetrant test.
In this context, it should also be noted that there is a European set of standards for determining the suitability of test equipment for penetrant testing and magnetic particle testing:
- In these standards on test equipment, their quality is assured through sample tests, batch control and monitoring of the application
- The test sensitivity is one of the most important properties for the recognizability of the display
- At the same time, however, it is difficult to determine the ad recognizability of a procedure
- The visibility of advertisements generally depends on the size and viewing conditions
- There is the absolute and the relative evaluation of proficiency tests according to the European standards
- Sample testing of test equipment systems for penetrant testing
- with a reference body according to EN ISO 3452-3
- with a sample test according to EN ISO 3452-2
- here at this link you will find the contribution to the DGZfP annual conference 2001 with the discussion and the conclusions for the reproducible and comparable evaluation of penetrant systems according to the standard
- at www.leak-detection-shop.com you will also find an amount for Importance of the UV lamp on the test result , which is also used in the fluorescent penetrant testing has a high relevance
Methods and specific procedure for the dye penetration process (water / emulsifier / solvent)
Method “A”: washing off with water
- Pre-cleaning
- Apply penetrant (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Wash off (water temperature at 10-38 ° C)
- Bring up developers
- Alcohol-based developer: first dry, then spray on the alcohol-based developer
- Water-based developer: apply water-based developer, then dry
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Inspection of the surface (illuminance at least 500 lux)
Method “B”: Post-emulsification with lipophilic emulsifier
- Pre-cleaning
- Apply penetrant (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Emulsifying
- Wash off (water temperature at 10-38 ° C)
- Bring up developers
- Alcohol-based developer: first dry, then spray on the alcohol-based developer
- Water-based developer: apply water-based developer, then dry
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Inspection of the surface (illuminance at least 500 lux)
Method “C”: wipe with the solvent-soaked cloth
- Pre-cleaning
- Apply penetrant (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C or 52-177 ° C for high-temperature penetrant)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Wipe with the solvent-soaked cloth (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C or 52-177 ° C for high-temperature penetrants)
- Spraying on the alcohol-based developer (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C or 52-177 ° C for high-temperature penetrants)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Inspection of the surface (illuminance at least 500 lux)
Method “E”: water and solvents can be removed
- Wash off with water first
- Then wipe it off with the cloth slightly dampened with solvent
Source: Docplayer.org PDF work steps for the penetration test, p. 2
Methods and specific procedure for the fluorescent penetration process (water / emulsifier / solvent)
Method “A”: washing off with water
- Pre-cleaning
- Apply water-washable penetrant (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Wash off (water temperature at 10-38 ° C)
- Bring up developers
- Non-aqueous developer or dry developer: first dry, then apply the developer
- Water-based developer: apply water-based developer, then dry
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Inspection of the surface (UV-A lamp with 1000 μW / cm², ambient lighting max. 20 lux)
Method “B”: Post-emulsification with lipophilic or hydrophilic emulsifier
- Pre-cleaning
- Apply post-emulsifiable penetrant (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Emulsify
- Method “B” lipophilic emulsifier: immerse for less than 3 minutes
- Method “D” hydrophilic emulsifier: first pre-wash at a water temperature of 10-38 ° C, then emulsify with an immersion concentration of 17-20% under 2 minutes or with a spray concentration under 5%
- Wash off (water temperature at 10-38 ° C)
- Bring up developers
- aqueous developer or dry developer: first dry, then apply the developer
- Water-based developer: apply water-based developer, then dry
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Inspection of the surface (UV-A lamp with 1000 μW / cm², ambient lighting max. 20 lux)
Method “C”: wipe with the solvent-soaked cloth
- Pre-cleaning
- Apply penetrant (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C)
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Wipe with the solvent-soaked cloth (temperature of the test surface at 10-52 ° C)
- Application of the aqueous developer or the dry developer
- Application time at least 10 minutes
- Inspection of the surface (UV-A lamp with 1000 μW / cm², ambient lighting max. 20 lux)
Source: Docplayer.org PDF work steps for the penetration test, p. 7
Consumables for dye penetrant testing and the fluorescent penetrant test (general: PT penetrant testing)
We look forward to your inquiry!
You are also welcome to contact us by phone or email.
Direct contact:
SECU-CHEK GmbH
An der Fähre 9
66271 Kleinblittersdorf
GERMANY
Phone +49 6805-942859-0
Fax +49 6805-942859-95
Email: info@secu-chek.de